MongoDB Atlas vs. self-hosted MongoDB quick guide.
It is plain as day that MongoDB has been a popular database solution for many applications in the recent past. One may argue this is due to its flexibility, scalability, and ease to use. However, Organizations are faced with opting for MongoDB Atlas, a fully managed cloud-based database service, or having MongoDB set up and hosted on their infrastructure.

MongoDB Atlas: The Managed Cloud Solution
MongoDB Atlas is a fully managed cloud database service offered by MongoDB Incorporation. It is a fully paid version of MongoDB and integrates natively with Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). As a developer, MongoDB Atlas’ Database-as-a-Service (DaaS) model enables you to use a robust document data model for high availability, scalability, and security with a unified query interface. In a nutshell, the main benefit of MongoDB Atlas is simplifying database management. The following are a few of the main benefits of using MongoDB Atlas:
Pros of using MongoDB Atlas:
Ease of use and deployment
MongoDB Atlas allows developers to focus on their applications rather than the infrastructure of their applications. Setting up, managing, and scalability of your MongoDB databases will not be part of your routine. It worsens if you have to be woken up at 3 am twice a month because of a database outage. Such problems can be avoided by having MongoDB Atlas get the job done. The ease of use also affects the platform’s ability to offer seamless scalability. That way, organizations can adjust their cluster size to accommodate the varying workloads. The platform provides a user-friendly interface and automation tools that streamline the deployment process and everyday operations.
Security and Compliance
Security is on top of the list of offerings by MongoDB Atlas. If you are worried about a third party digging into your data, MongoDB Atlas is your go-to solution. It complies with industry standards like SOC 2, HIPAA, and GDPR. That way, if your organization has strict regulatory requirements, the platform is the ideal fit for you. Some of the security features applied by MongoDB Atlas are encryption at rest, encryption at transit, and fine-grained access control. Also, it allows you to configure network access controls to restrict incoming connections to your database cluster.
Backup and Recovery
Backup and recovery are non-negotiable features when handling any form of data. Data loss could be devastating to an organization, so MongoDB Atlas offers automated backups with point-in-time recovery. The process is also user-controlled, as one can schedule backups. The recovery mechanism is also simplified hence making the platform data-loss-proof. Additionally, MongoDB Atlas includes backups in the price, so there's no need to pay extra to lease dedicated servers to store backup copies.
Cons of using MongoDB Atlas:
Cost
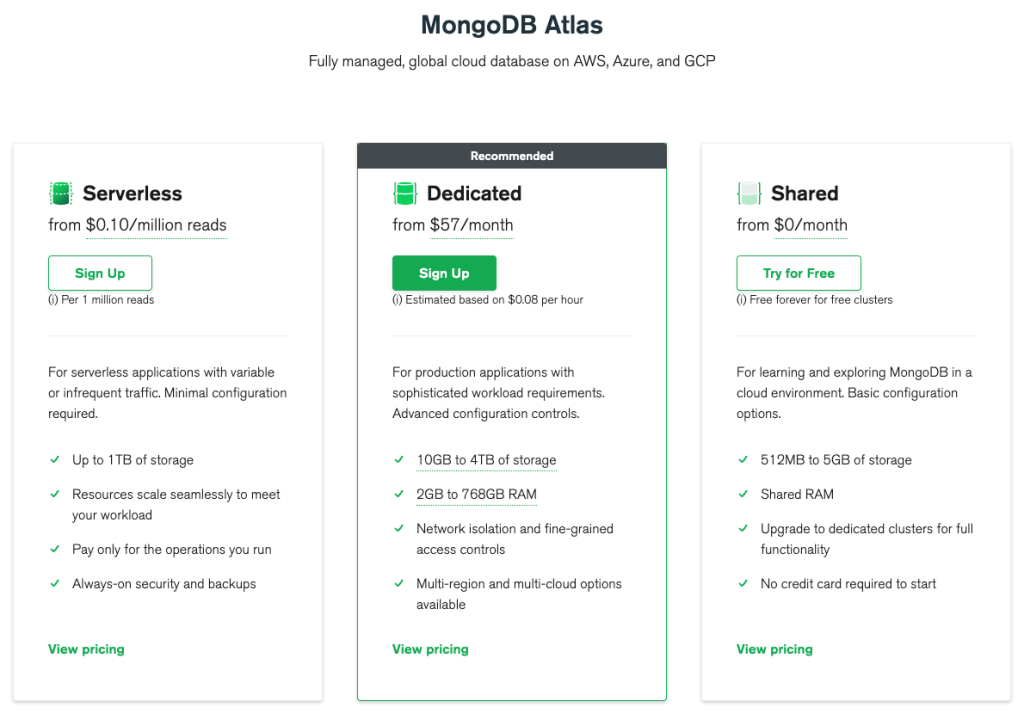
The major downside of using MongoDB Atlas is that the outstanding features discussed above come at a cost. It is upon your organization to determine whether the convenience offered by the platform supersedes the cost of the service. MongoDB Atlas charges per hour of cluster usage. The charges vary based on your cloud provider implying using AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud will attract varying costs. Also, cluster size, cluster region, data transfer costs, and types of services added play a role in determining your cost. Additional services include backups and restores, custom storage speed, and advanced training or support plans.
Limited control and dependency on the cloud provider
If the cost of the MongoDB Atlas plan is not a deal breaker for you, the limited control and dependency on the cloud provider should not be a deal breaker either. However, for what it's worth, you will have to work with the available infrastructure. There is restricted access to specific configurations. However, this is only a problem whereby businesses have specific requirements for their database environment. Additionally, if there are any disruptions on the provider’s end, you will be equally affected.
Self-Hosted MongoDB: Taking control of your database
Unlike a managed cloud solution, self-hosted MongoDB requires deploying and managing a MongoDB instance on your infrastructure or a chosen hosting provider. There is much control with this alternative, especially if you create your infrastructure. However, additional effort and numerous hours are spent on database management, which could have otherwise been used in other routine activities. While we are here, we might as well explore the pros and cons of this approach:
Pros of Self-Hosted MongoDB
Cost efficiency
Cost efficiency when using self-hosted MongoDB is a controversial factor. However, self-hosted MongoDB may be the best alternative for small-scale applications and organizations. For instance, if you have a limited budget or run operations by yourself, it is essential to avoid costs associated with MongoDB Atlas. Also, at this point, the data is not as bulky, making it easier to manage. You can find cost-efficient shared hosting for your business and then embrace the self-hosted MongoDB path.
Flexibility and data sovereignty
You will enjoy flexibility with self-hosted MongoDB because there are no pre-defined infrastructures. It is, therefore, an excellent alternative for a business specific to how it wants its data aligned. You can also control hardware requirements, network configuration, and security requirements. You can optimize the database environment to meet specific performance requirements. While at it, if your organization has strict data sovereignty requirements, self-hosted MongoDB is your go-to option. That way, you can have complete control over the location of your data.
Cons of Self-Hosted MongoDB
Administrative overhead
As stated above, with self-hosted MongoDB, a proportion of hours will be invested in database management. There is a need for skilled personnel to engage in tasks such as hardware provisioning, software installation, configuration, monitoring, and maintenance. Organizations must allocate resources and expertise for this responsibility to be executed effectively.
Backup and disaster recovery
Organizations need to ensure there are reliable backup and recovery systems in place when using self-hosted MongoDB. Once again, this is putting person-hours into business aspects that a third party can execute. Any system error may be detrimental to the organization. Schedules need to be maintained; replication needs to be managed, and testing recovery procedures in place.
Scalability and availability
This process is more complex when using a self-hosted MongoDB than MongoDB Atlas. Hardware needs must be considered, which could have been avoided by using a third party for the service. Other factors that must be factored in are sharding configuration and load balancing. All these interventions are in a bid to attain availability and fault tolerance.
The Decision Dilemma: Self-Hosted vs. MongoDB Atlas
The truth is that there is no definitive “right” or “wrong” answer when comparing MongoDB Atlas and self-hosted MongoDB. The choice of the approach taken solely depends on the needs of the organization. This is because both options have advantages and trade-offs; hence what may be ideal for one organization may not work for another. You can choose the choice that best meets your organization's needs by being aware of the significant differences. It would be best if you also took into account aspects like deployment ease, scalability, maintenance requirements, and cost-effectiveness.